
Why should you join our Funded Trader Program?
- Fully funded trading account.
- Big profits 50-50 % profit split.
- Mobile International Trading.
- You’re not liable to losses.
- 10% Drawdown.
- Robust Technology and Deep Institutional Liquidity.


Forex Trading for Beginners
The United States is one of the world’s most important markets for trading currencies. The US dollar is widely used as a reserve currency, which makes it attractive for foreign investors to invest in US companies that use the dollar as their primary currency. The US dollar has also offered a lot of opportunities to foreign investors. However, there is still more to be understood about the currency, especially when it comes to forex trading tax US laws.
The truth is that the US has a very complicated tax system. There are a lot of rules and regulations, so it’s important to have a good understanding of how this system works before you begin trading. The first thing you should know is that forex trading is considered a business activity in the US, which means that you’ll have to pay taxes on your profits. You also need to consider whether you’re allowed to take advantage of any tax deductions or credits available to traders. This might depend on your circumstance or even the company you are trading with.
As a forex trader, you should not only think about profits. You should also think about other things that may arise along the way, like taxes. Tax on forex trading US is not something to be taken lightly, as there are rules set to ensure every US trader pays taxes on their profits. Read on to understand more about forex trading taxes in the United States.
The United States has a long history of regulating currency trading. The country’s legal framework for forex trading is complex, but the IRS has issued several rulings to clarify its position on taxation in the sector. As with any other type of trading, there are certain rules that you have to follow when you want to trade on forex markets. So, is forex trading tax-free?
As with any transaction involving currency, you should always report your profits and losses on your tax return. Whether you are buying or selling foreign currencies, you will need to report income from foreign currency transactions on your Form 1040 or Form 1040NR and declare an amount equal to the total gross profit realized from the transaction when you file your return. If you use some form of tax sheltering such as hedging or arbitrage strategies, then the IRS will treat these gains and losses differently than ordinary income and losses.
Generally, it is wise to understand US tax laws on forex trading to know what to expect as you begin your trading journey. At first, everything might seem complicated, and you may not even understand some things. The good news is that there are tax consultants and forex trading professionals who can help you understand how forex trading taxes work in the US.
If you have been in the forex industry for a long time, one of the most common questions you will hear from newbies is; Do you pay tax on forex trading US market. The answer is yes. Forex traders are required to pay tax on their profits. Forex trading is considered a business, so the profits from forex trading are taxable.
Normally, forex traders are subject to income tax in the country where they live, and that is the same case when you come to the United States. American citizens who trade using forex brokers outside the United States must also pay taxes on their profits earned in foreign currency. This is true even if the trader does not reside in the United States at all times and only trades online with a broker located overseas.
When a trader wins money in foreign currency, it is considered income when converted into US dollars but an expense when converted back into foreign currency. The exchange rate between currencies determines how much taxable income is earned when converting funds into US dollars or vice versa.
A forex trader can also be subject to capital gains tax when selling a position that has lost value over time through market volatility or other causes such as bankruptcy of the brokerage firm handling their account.
Forex trading income tax is taxable income earned from foreign currency trading. It has been classified under the personal income tax slab, which means it is taxed at a higher rate than normal salary income.
The amount of forex trading income tax an individual pays depends on their total annual foreign currency earning and their marginal rate of personal income tax.
Corporation tax is a tax on the profits of companies. Companies pay corporation tax on their profits after they have been taxed at the personal income tax rate. The forex trading corporation Tax is imposed on all kinds of organizations engaged in foreign exchange transactions. It is levied at different rates depending upon the nature of business, the transaction, and the source from which the income is generated.
Capital gain is the profit you make when you sell your investment. It is also what you get from selling an asset for more than you bought it for or receiving payment for that asset.
Forex traders who have made profits on their investments may be subject to capital gains tax when they sell their assets. This tax is usually calculated as a percentage of the profit gained from selling an asset. The capital gain tax rate in most countries is between 28 and 35 percent, although there are some exceptions to this rule.
In the United States, Forex stamp duty reserve tax is a tax imposed on the value of financial contracts not denominated in US dollars. The tax applies to any transaction of interest rate swaps, foreign exchange swaps, and options, including whether or not the swap or option is entered into by an investment company registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940. The tax also applies to transactions involving commercial paper, bonds, and debentures issued by foreign issuers.
Forex traders are taxed very differently in the USA, depending on the type of trading they do. This is because forex trading has a lot of different tax implications, as there are many different types of trades that can be made. Some of the ways the IRS collects taxes from forex include;
Apart from that, USA forex traders can choose to file their tax returns under the laws stated in section 988 or section 1256.
Do I pay tax on forex trading US dollars? As mentioned earlier, forex traders should pay taxes on the profits they make in the foreign exchange market. They can file their earnings under the laws stated in section 988. The law simply puts that all capital gains made in the FX market will be classified as ordinary income and taxed.
It is also worth mentioning that the United States tax code clearly distinguishes between the long-term and short-term forex gain. This means that you will be charged depending on your annual earnings. The long-term tax gains can range between zero to 20%. Here is a simple 2020 forex trading tax reporting that illustrates the tax brackets in the United States;
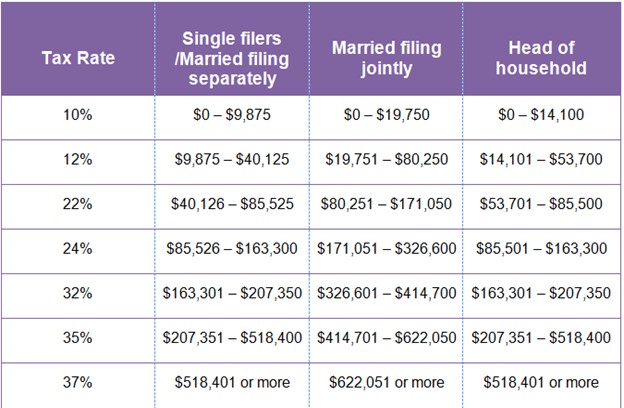
It is not necessarily that you file your tax returns under section 988. You can also use section 1256 to successfully file your gain and losses tax returns. Under this section, your 60% annual earnings will be taxed at a constant or fixed rate of 15%. On the other hand, 40% will undergo taxation, depending on your income bracket. Normally, section 1256 is a good option for those traders with an income bracket of 22%.
Forex trading is an industry that requires discipline, patience, understanding, and dedication. However, when it comes to forex taxation, there are a few things you will need to keep in mind other than dedication and focus. These things may include;
If you are new to trading, ensure you have filed your taxes earlier to avoid forgetting about them. The IRS will assess your tax records, and you do not want to get a penalty for delaying or not paying your taxes.
The best way to ensure you have good tax records is to make sure that you file your tax returns as soon as possible after the end of the tax year. By filing early, you can ensure that any payments made by the IRS are accurate and reflect all of the information on your return accurately. If there are any issues with these payments, you may need to contact an accountant or tax consultant about what needs to be done for these issues to be resolved.
How can I avoid taxing on day trading US broker? Many traders are always finding ways to avoid taxes. However, you will need to file your return yearly if you have a huge income. The good news is that there are ways to get around taxes legally. One is by using reduction strategies or minimizing your trading expenses.
Avoiding paying taxes may not be wise because the IRS will eventually catch up with your tricks. Therefore, it is important to file all your returns to avoid trouble and huge penalties in the future.
This will depend on your annual earnings. Most traders are usually taxed 15% of the total profits in the forex market.
It is usually advisable to stick to section 988 if you have losses in forex trading since it is more favorable than section 1256.